Hybrid Integration
You do not need to move all your IT systems to the cloud. You can keep and maintain some sensitive or legacy applications data within your organization, which we will call on-premises data.
You can even host your own cloud, called a private cloud, and keep the security of your own infrastructure. You can even hire a third party vendor to maintain this private cloud. Regardless of your plans, you do not need to use a public cloud, a cloud hosted and maintained by a third party.
Either way, hybrid integration is the communication link between all of these platforms, and many firms prefer it over putting everything they have in the cloud. This approach gives them the advantages of cloud computing while giving them complete control over their sensitive data and privacy.
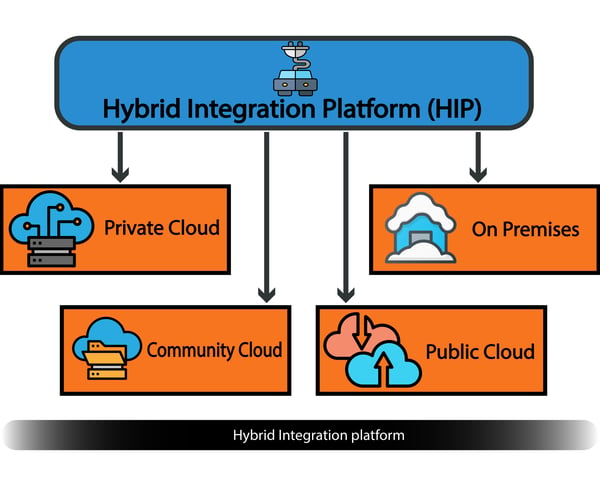
Figure -1, Hybrid Integration platform
More details are available in these references:
Hybrid cloud integration Platform and solutions
Understanding Hybrid Integration Platforms
How hybrid integration happens?
Hybrid integration platforms happens in multiple levels and across different type of architecture as in the reference in Enterprise Application Integration
- Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)
- Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)
- Managed APIs
- Data Integration
- Identity and access control
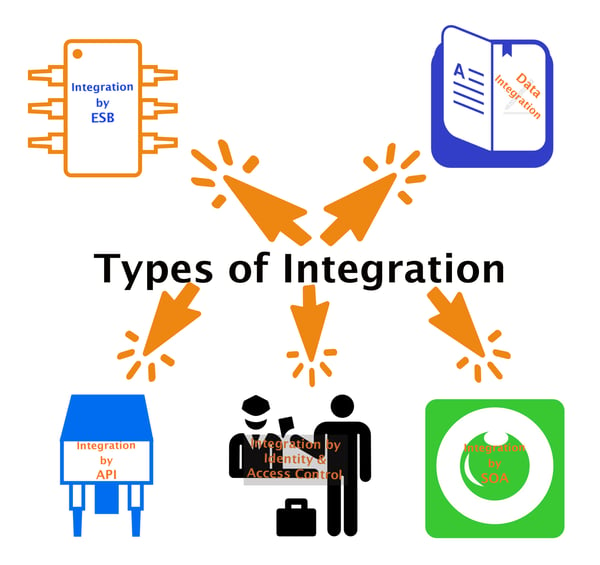
Figure -2, Types of Integration
Services level Integration (SOA)
Most companies usually move their SOA operations to the cloud first. The cloud gives them a cost-effective solution for their infrastructure needs through one of three different cloud formats. These formats are infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a service (PaaS), and Software as service (SaaS).
IaaS is the most basic cloud service, providing IT infrastructure, servers, virtual machines, storage, networks, and operating systems.
PaaS is an on-demand environment for development, testing, delivery, and application management. Developers can quickly create web or mobile applications without worrying about the set up. It also inherently uses IaaS.
iPaaS is integrated platform as a service helps in integration across multiple layers.
SaaS clouds host and manage software applications and the underlying infrastructures in the natural security and data compliance of the cloud.
Regulatory Compliance & Security: Some enterprises must keep their data on premises for compliance. Some organizations keep their data on-premises for security. Either way, you must have a plan for maintaining your non-sensitive data in cloud and your sensitive data on premises. Therefore, you must connect your infrastructure to the cloud to get the advantages of cloud computing.
It is estimated that the average reduction of total cost of ownership (TCO) among cloud adopters across four key industries, is 40 percent: These industries are technology, financials, manufacturing and communications according to the report Hybrid Cloud: 10 notable statistics
Service oriented (other types)
The other types include Web services implementation, Service oriented integration. These WS-* specifications provide interoperable protocols for reliable messaging, transaction and security in loosely coupled fashions. They are built on top of SOAP and XML standards.
Integration through Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)
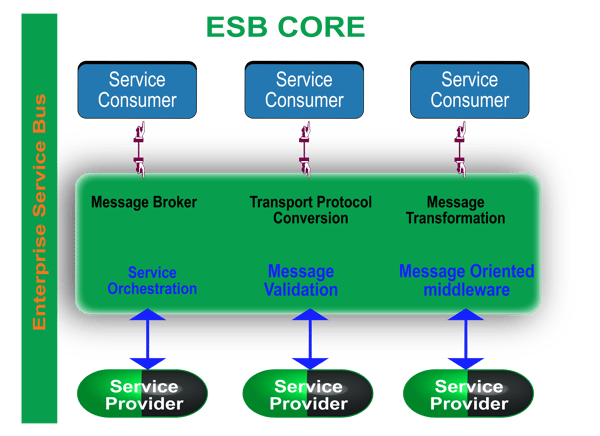
Figure 3, ESB
Enterprise service bus (ESB) was created to handle this hybrid integration. It links together your middleware message broker and your SOA to address the needs of both in a simple but effective way that takes full advantage of the cloud.
Because you have multiple open source and proprietary ESB vendors available to you such as Dell Boomi, WSO2, Talend ESB, IBM Websphere ESB , Microsoft Biztalk server and many others, You must choose the right ESB tool based on your needs, architectural capabilities, and the cost effectiveness of the solution.
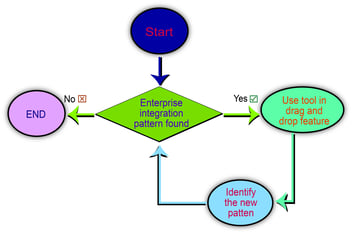
How much enterprise service bus handles integration depends on its capability to address the enterprise integration pattern.
What is enterprise integration pattern? All applications, businesses, data, and infrastructure, follow patterns in communication. They are about 65 of these patterns in use worldwide, which you can reuse as templates for your integration initiatives.
The following sample list showcases a few of the patterns that come built into WSO2 ESB.
|
Routing Slip |
When the order of the route path is not clear in design time, how to route messages sequentially through small steps |
|
|
Process Manager |
When the required number of steps is not clear in design time, how to route messages through multiple processing steps. |
|
|
Message Broker |
How to disconnect destination of the message from the sender and maintain the central control of flow of messages. This is referred as loosely coupled. |
|
|
Message Bus |
This is a middle tier architecture in which individual applications work together in loosely coupled manner. so that, one application can be removed without impacting for the other applications. |
|
|
Message Router |
How to disconnect individual processing sequences so that message is parsed in proper filters depending on the situation. |
|
Correlation Identifier |
How the requester understands which reply it is meant for, when it receives the response. |
|
|
Message Sequence |
How the messaging can send a large amount of data arbitrarily |
|
|
Message Expiration |
How the sender communicates which one should be considered expired; so that there is no processing. |
Integration through Managed APIs
WSO2 API Manager is a complete solution for creating, publishing and managing all aspects of an API’s life cycle.
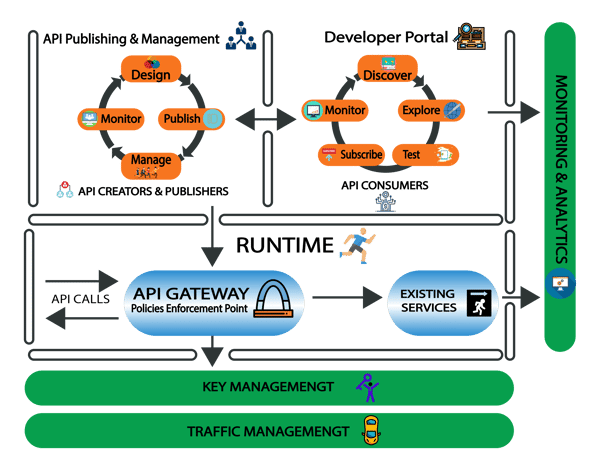
Figure-4, APIs
Figure -4 shows how the API manager components work.
You need to publish APIs and subscribe to them from within API Manager before you can use them., Fortunately, API manager provides a simple interface for API creators to develop, document, scale, version, and publish APIs.
You can also find, evaluate, and subscribe APIs for your organization through the API store. The API store provides a secure collaborative interface for API publishers to host, advertise, and authenticate their APIs.
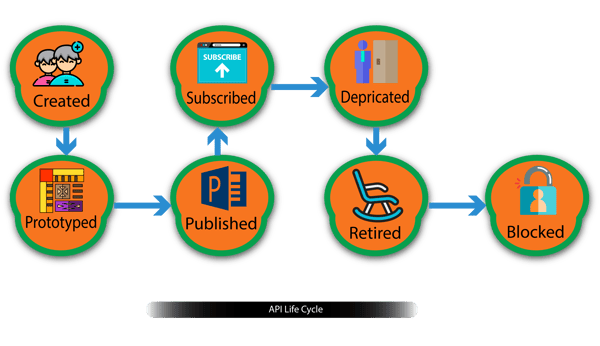
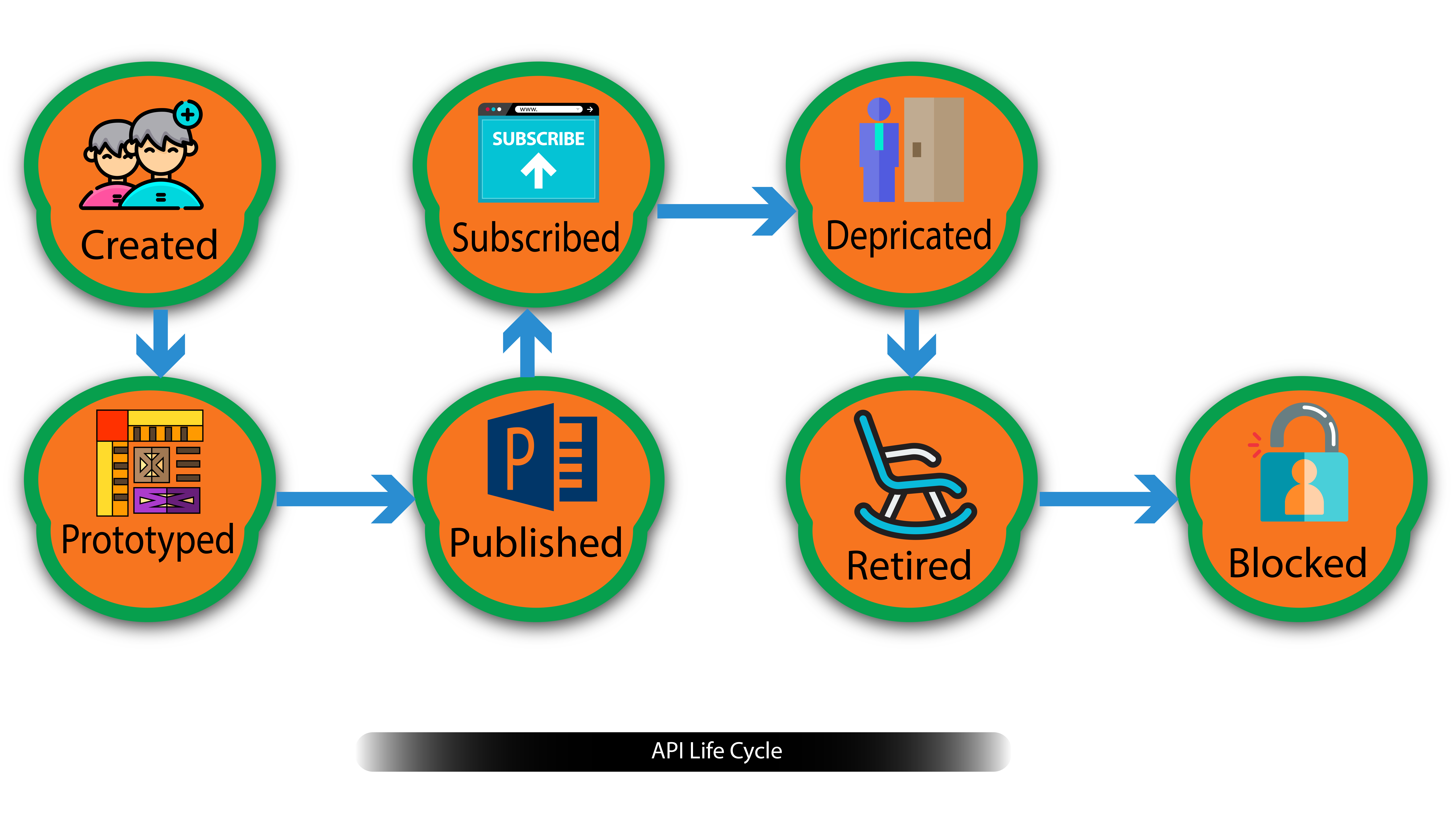
Figure-5, API Life cycle.
APIs have their own life cycles which are independent to the backend services they rely on. These life cycles generally come in multiple different stages which include CREATED, PROTYPED, PUBLISHED, DEPRICATED, RETIRED, and BLOCKED. You will find the current life cycle state of an API on the API publisher web interface and managed by the API publisher role.
Data integration
It combines technical and business processes to collect data from disparate resources into valuable and meaningful information.
Data integration is handled by WSO2 DSS Server and WSO2 DAS server. Data governance is taken care by governance registry.
Identity and access control
WSO2 business activity monitor (BAM) and API manager and identity server takes are of security, authentication and access roles.
WSO2 Enterprise integrator version 6 comes as a single package with a number of modules and profiles .
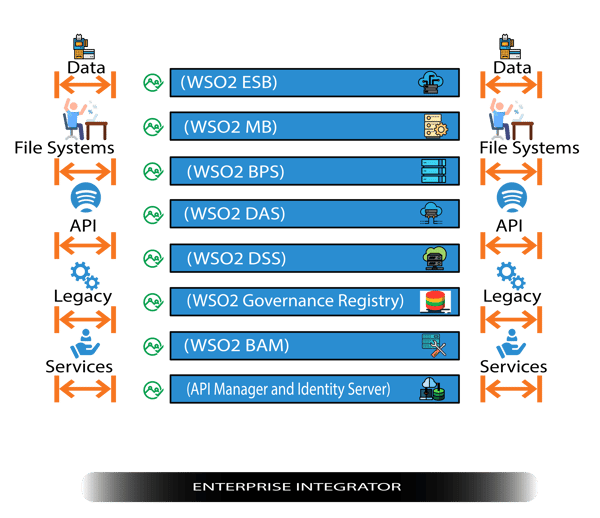
Figure 6
These modules include:
- ESB Service Integration (WSO2 ESB)
- Message broker(WSO2 MB)
- Business process(WSO2 BPS)
- Micro-services and Analytics.
- Real-time data processing (WSO2 DSS)
- WSO2 Governance registry
- WSO2 business activity monitor (BAM)
- API manager and identity server
The profiles of these modules in enterprise Integrator is configured as a single product which helps in hybrid integration in quite simpler process. More information is available in WSO2 Library
Reference:
Hybrid cloud integration Platform and solutions
Understanding Hybrid Integration Platforms
Enterprise Application Integration
Hybrid Cloud: 10 notable statistics


Leave a Comment