SAP SuccessFactors was founded in 2001 and acquired by SAG AG’s US subsidiary, SAG America, in 2011. It provides Human Capital Management (HCM) cloud solutions, covering the needs of 45 million people/employees in more than 6,000 organizations worldwide, according to Gartner, Forester and IDC.
HCM features
SAP SuccessFactors HCM suites support all your HR activities and processes, such as core HR, payroll, talent, and workforce management in a single unified platform with analytical and dashboard capabilities, through serval HR software modules.
Some of these modules include:
- Core HR and Payroll
- Time and attendance
- Learning and development
- Performance and competition
- Recruiting and on-boarding
- Workforce planning and analytics
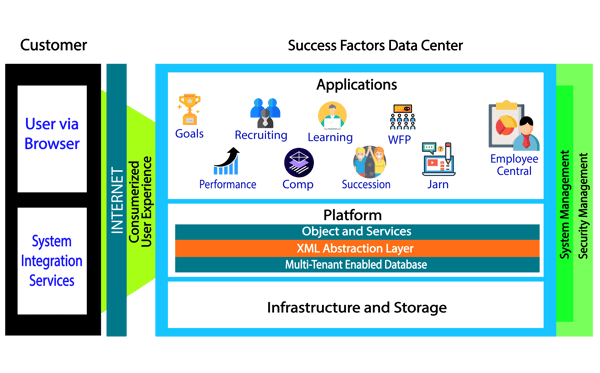 Image 1: SAP SuccessFactors
Image 1: SAP SuccessFactors
While HR has been a quick adopter of cloud based solutions - and this trend is on-going as it is noted here and here-, factors such as quick and easy adoption to changes in local regulations, along with technical limitations, may lead to a hybrid environment with both on-premise and cloud components.
Fortunately, many HCM platforms come with the following options:
- Point-to-point integration. While effective for small environments with limited interfaces, the interfaces can become chaotic, not-easily managed, and expensive
- On-premise integration platform. Although this is an integrated and robust solution, it does not provide flexibility and low cost of ownership, requiring large-scale operations that have the IT resources to support it
- Cloud-based integration (iPaaS platforms) enabling development, executing and governance of integration flows. This option provides the flexibility you need with the low cost of ownership you want, without needing significant IT resources.
SAP SuccessFactors also provide open, industry-standard integration, technologies, API, and events.
Extending SAP SuccessFactors Functionality
You can extend SAP SuccessFactors’s functionality by integrating it with other HRM applications with the following functions:
Payroll
Payroll application is one of the most important functions of HR as every employee should be paid accurately and on-time.
|
Application Features |
|
|
Integration Features |
|
|
Business processes |
|
Identity Management
Employee changes should be interfaced with the directory service as the identity management source.
|
Application Features |
|
|
Integration Features |
|
|
Business processes |
|
Benefits Management
Benefits may include health and life insurance, stock options, leased cars, etc. which may or may not be provided by different partners.
|
Application Features |
|
|
Integration Features |
|
|
Business processes |
|
Time Management
Including simple clock-in, clock-out systems up to advance access control systems, all provide employee time attendance information.
|
Application Features |
|
|
Integration Features |
|
|
Business processes |
|
Pre-hire Screening
HR often uses recruitment agencies to evaluate candidates.
|
Application Features |
|
|
Integration Features |
|
|
Business processes |
|
ERP
ERP and HCM are major systems within an organization, and you can integrate them in several ways.
|
Application Features |
|
|
Integration Features |
|
|
Business processes |
|
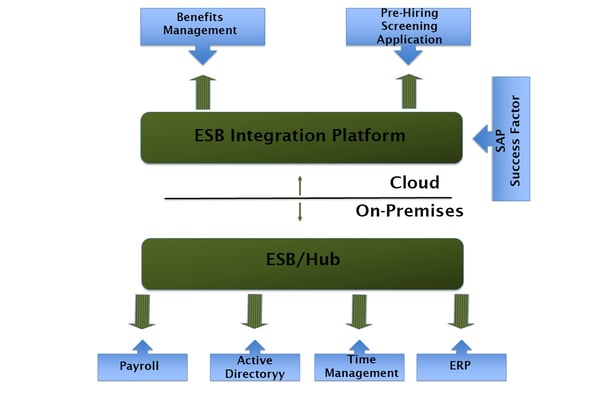
Image 2: A typical SAP Success Factors integration
Key factors for SAP SuccessFactors Integration
Every integration project faces challenges during implementation. The major challenges for SuccessFactors integration are illustrated below:
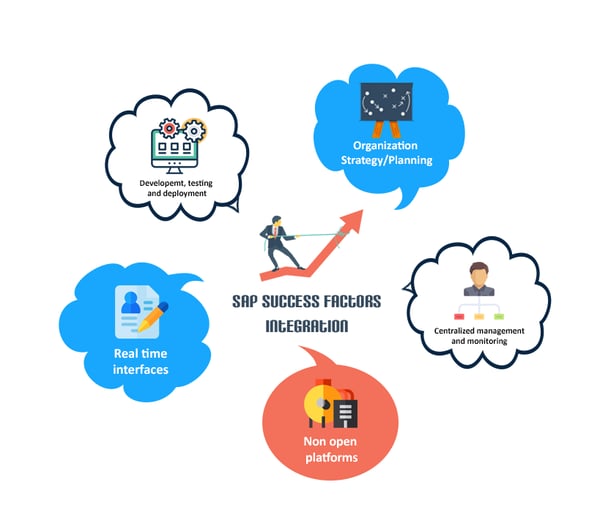
Image 3 : Major factors for Success factors integration
Organization Integration Strategy / Planning
With Cloud-based applications, such as SAP SuccessFactors, you should consider the integration platform architecture first. Often taken for granted, point-to-point is not an option in projects of this scale. Therefore, you must choose between hosting your own integration platform on site or going with a cloud-based one (iPaaS). Cloud-based solutions provide several benefits over on-premise ones, but your final decision should depend on:
- Alignment with your organization’s integration strategy
- Total cost savings, including ownership costs, operational costs, consulting fees etc
Centralized management and monitoring
HCM integration may cover a variety of platforms and applications, hosted either on your own network or the cloud. Additionally, you may do it within your own organization or across your partners.
Enabling the central monitoring and management feature assures your ability to recognize and troubleshoot issues. It also provides traceability and log features (such as execution points, duration, data in a drill down manner) that will be helpful in terms of auditing.
Not integrating open platforms
Depending on your local laws and adoption level, your payroll systems may be the leader in your market, but not the technology used. Also, while time attendance systems measure time events accurately, they may have not focused on technology evolution.
In all these cases, you may need to strongly customize your integration with HCM.
Real-time Interfaces
Real-time interfaces may be key factors in the performance and availability of your integration platform. Processes such as employee disembarkment, are time critical since the user locking should be initiated in real time in every involved system.
Availability may also be important on batch mode interfaces. Your organizations may have large data volumes which may slow down integration performance even in batch mode.
Developing, Testing and Deploying
Development should be easy and quick, and should be done using high level tools that provide reusability based on industry standards. Testing should be performed in quality environments when feasible, and in simulation when not.
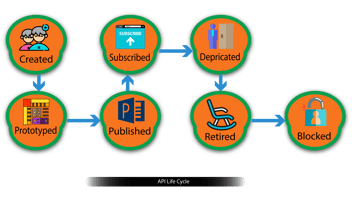
Your integration platform should also provide deployment methods so you can push any newly develop modules into your production environment as quickly as possible (eg a publish/subscribe mechanism between testing and production).


Leave a Comment